var http = require("http");var fs = require("fs");http.createServer(function(req, res) {res.setHeader("status", "200 OK");res.setHeader("Set-Cookie", "isVisit=true;domain=.yourdomain.com;path=/;max-age=1000");res.write("Hello World");res.end();}).listen(8888);console.log("running localhost:8888")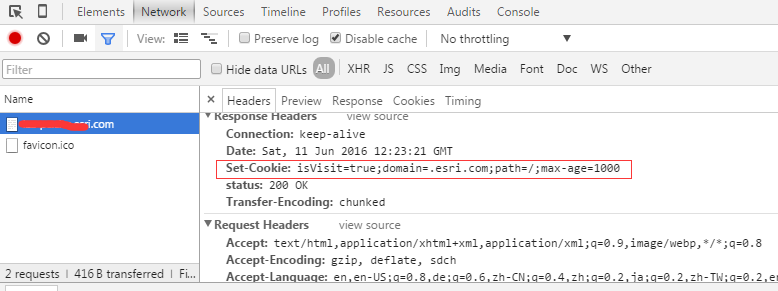
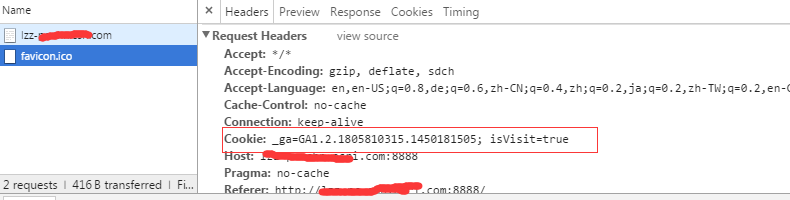
直接设置Set-Cookie过于原始,我们可以对cookie的设置过程做如下封装:
var serilize = function(name, val, options) {if (!name) {throw new Error("coolie must have name");}var enc = encodeURIComponent;var parts = [];val = (val !== null && val !== undefined) ? val.toString() : "";options = options || {};parts.push(enc(name) + "=" + enc(val));// domain中必须包含两个点号if (options.domain) {parts.push("domain=" + options.domain);}if (options.path) {parts.push("path=" + options.path);}// 如果不设置expires和max-age浏览器会在页面关闭时清空cookieif (options.expires) {parts.push("expires=" + options.expires.toGMTString());}if (options.maxAge && typeof options.maxAge === "number") {parts.push("max-age=" + options.maxAge);}if (options.httpOnly) {parts.push("HTTPOnly");}if (options.secure) {parts.push("secure");}return parts.join(";");}需要注意的是,如果给cookie设置一个过去的时间,浏览器会立即删除该cookie;此外domain项必须有两个点,因此不能设置为localhost:something that wasn"t made clear to me here and totally confused me for a while was that domain names must contain at least two dots (.),hence "localhost" is invalid and the browser will refuse to set the cookie!服务器端解析cookie
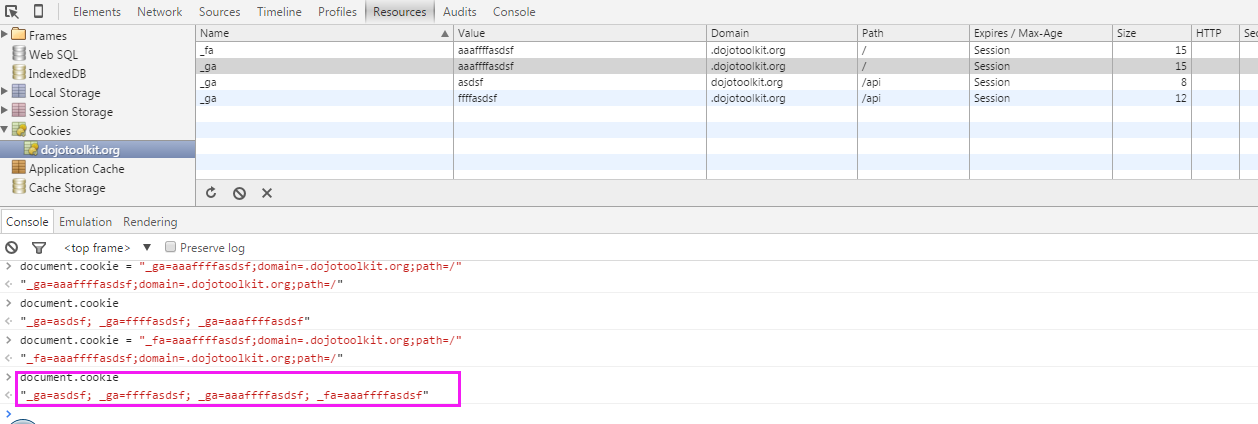
所以当前端传递到服务器端的cookie有多个重复name value时,我们只需要最匹配的那个,也就是第一个。服务器端解析代码如下:
var parse = function(cstr) {if (!cstr) {return null;}var dec = decodeURIComponent;var cookies = {};var parts = cstr.split(/s*;s*/g);parts.forEach(function(p){var pos = p.indexOf("=");// name 与value存入cookie之前,必须经过编码var name = pos > -1 ? dec(p.substr(0, pos)) : p;var val = pos > -1 ? dec(p.substr(pos + 1)) : null;//只需要拿到最匹配的那个if (!cookies.hasOwnProperty(name)) {cookies[name] = val;}/* else if (!cookies[name] instanceof Array) {cookies[name] = [cookies[name]].push(val);} else {cookies[name].push(val);}*/});return cookies;}客户端的存取"name1=value1;name2=value2;name3=value3";当用来设置值的时候,document.cookie属性可设置为一个新的cookie字符串。这个字符串会被解释并添加到现有的cookie集合中。如:
document.cookie = "_fa=aaaffffasdsf;domain=.dojotoolkit.org;path=/"设置document.cookie并不会覆盖cookie,除非设置的name value domain path都与一个已存在cookie重复。
var cookieUtils = {get: function(name){ var cookieName=encodeURIComponent(name) + "="; //只取得最匹配的name,value var cookieStart = document.cookie.indexOf(cookieName); var cookieValue = null;if (cookieStart > -1) {// 从cookieStart算起var cookieEnd = document.cookie.indexOf(";", cookieStart);//从=后面开始if (cookieEnd > -1) { cookieValue = decodeURIComponent(document.cookie.substring(cookieStart + cookieName.length, cookieEnd));} else { cookieValue = decodeURIComponent(document.cookie.substring(cookieStart + cookieName.length, document.cookie.length));} }return cookieValue;},set: function(name, val, options) {if (!name) {throw new Error("coolie must have name");}var enc = encodeURIComponent;var parts = [];val = (val !== null && val !== undefined) ? val.toString() : "";options = options || {};parts.push(enc(name) + "=" + enc(val));// domain中必须包含两个点号if (options.domain) {parts.push("domain=" + options.domain);}if (options.path) {parts.push("path=" + options.path);}// 如果不设置expires和max-age浏览器会在页面关闭时清空cookieif (options.expires) {parts.push("expires=" + options.expires.toGMTString());}if (options.maxAge && typeof options.maxAge === "number") {parts.push("max-age=" + options.maxAge);}if (options.httpOnly) {parts.push("HTTPOnly");}if (options.secure) {parts.push("secure");}document.cookie = parts.join(";");},delete: function(name, options) { options.expires = new Date(0);// 设置为过去日期 this.set(name, null, options);} }缓存优点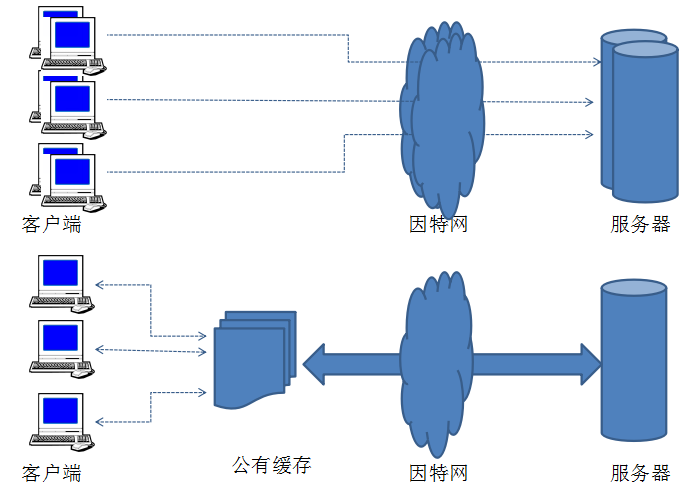
事实上在实际应用中通常采用层次化的公有缓存,基本思想是在靠近客户端的地方使用小型廉价缓存,而更高层次中,则逐步采用更大、功能更强的缓存在装载多用户共享的资源。
缓存处理流程
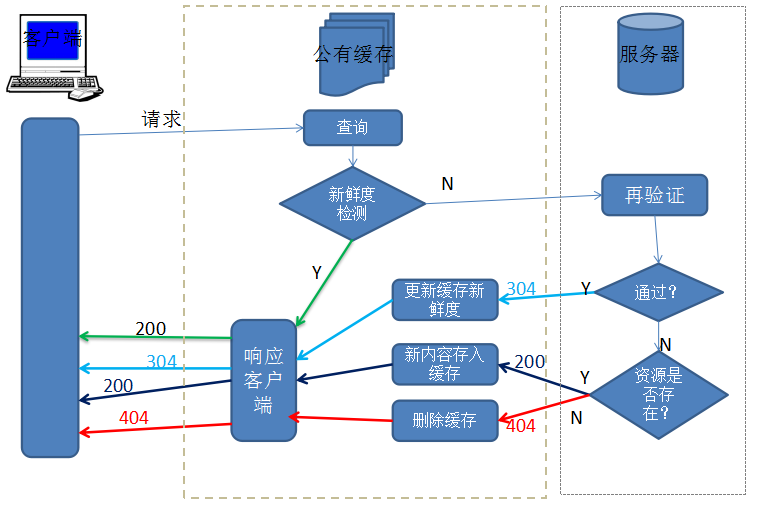
而对于前端开发者来说,我们主要跟浏览器中的缓存打交道,所以上图流程简化为:
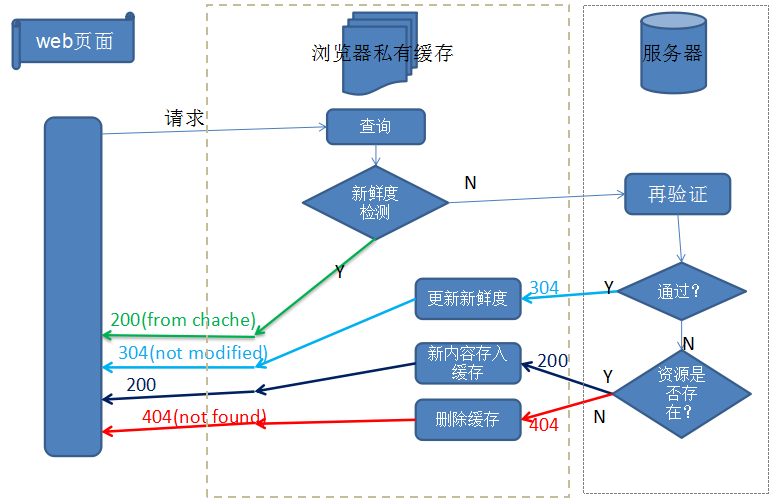
下面这张图展示了某一网站,对不同资源的请求结果,其中可以看到有的资源直接从缓存中读取,有的资源跟服务器进行了再验证,有的资源重新从服务器端获取。
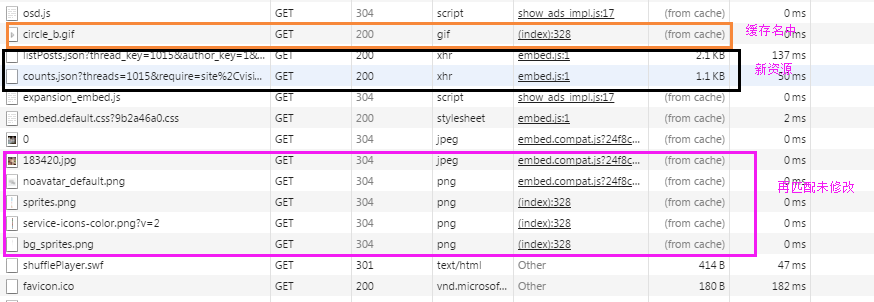
注意,我们讨论的所有关于缓存资源的问题,都仅仅针对GET请求。而对于POST, DELETE, PUT这类行为性操作通常不做任何缓存
新鲜度限值
HTTP通过缓存将服务器资源的副本保留一段时间,这段时间称为新鲜度限值。这在一段时间内请求相同资源不会再通过服务器。HTTP协议中Cache-Control和 Expires可以用来设置新鲜度的限值,前者是HTTP1.1中新增的响应头,后者是HTTP1.0中的响应头。二者所做的事时都是相同的,但由于Cache-Control使用的是相对时间,而Expires可能存在客户端与服务器端时间不一样的问题,所以我们更倾向于选择Cache-Control。
Cache-Control
下面我们来看看Cache-Control都可以设置哪些属性值:
max-age(单位为s)指定设置缓存最大的有效时间,定义的是时间长短。当浏览器向服务器发送请求后,在max-age这段时间里浏览器就不会再向服务器发送请求了。
<html> <head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=no" /><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=EDGE" /><title>Web Cache</title><link rel="shortcut icon" href="./shortcut.png"><script></script> </head> <body class="claro"> <img src="./cache.png"> </body></html>var http = require("http");var fs = require("fs");http.createServer(function(req, res) {if (req.url === "/" || req.url === "" || req.url === "/index.html") {fs.readFile("./index.html", function(err, file) {console.log(req.url)//对主文档设置缓存,无效果res.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache, max-age=" + 5);res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html");res.writeHead("200", "OK");res.end(file);});}if (req.url === "/cache.png") {fs.readFile("./cache.png", function(err, file) {res.setHeader("Cache-Control", "max-age=" + 5);//缓存五秒res.setHeader("Content-Type", "images/png");res.writeHead("200", "Not Modified");res.end(file);});}}).listen(8888)当在5秒内第二次访问页面时,浏览器会直接从缓存中取得资源
public 指定响应可以在代理缓存中被缓存,于是可以被多用户共享。如果没有明确指定private,则默认为public。
private 响应只能在私有缓存中被缓存,不能放在代理缓存上。对一些用户信息敏感的资源,通常需要设置为private。
no-cache 表示必须先与服务器确认资源是否被更改过(依靠If-None-Match和Etag),然后再决定是否使用本地缓存。
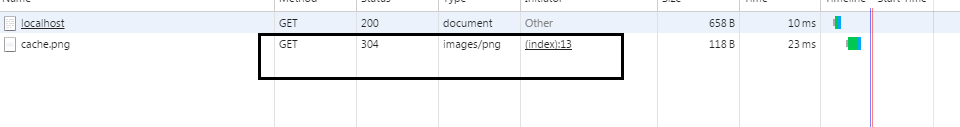
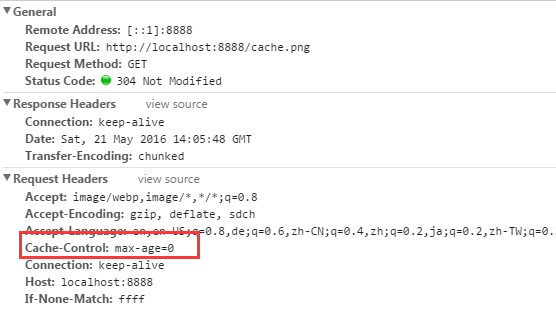
如果上文中关于cache.png的处理改成下面这样,则每次访问页面,浏览器都需要先去服务器端验证资源有没有被更改。
fs.readFile("./cache.png", function(err, file) {console.log(req.headers);console.log(req.url)if (!req.headers["if-none-match"]) {res.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache, max-age=" + 5);res.setHeader("Content-Type", "images/png");res.setHeader("Etag", "ffff");res.writeHead("200", "Not Modified");res.end(file);} else {if (req.headers["if-none-match"] === "ffff") {res.writeHead("304", "Not Modified");res.end();} else {res.setHeader("Cache-Control", "max-age=" + 5);res.setHeader("Content-Type", "images/png");res.setHeader("Etag", "ffff");res.writeHead("200", "Not Modified");res.end(file);}}});no-store 绝对禁止缓存任何资源,也就是说每次用户请求资源时,都会向服务器发送一个请求,每次都会下载完整的资源。通常用于机密性资源。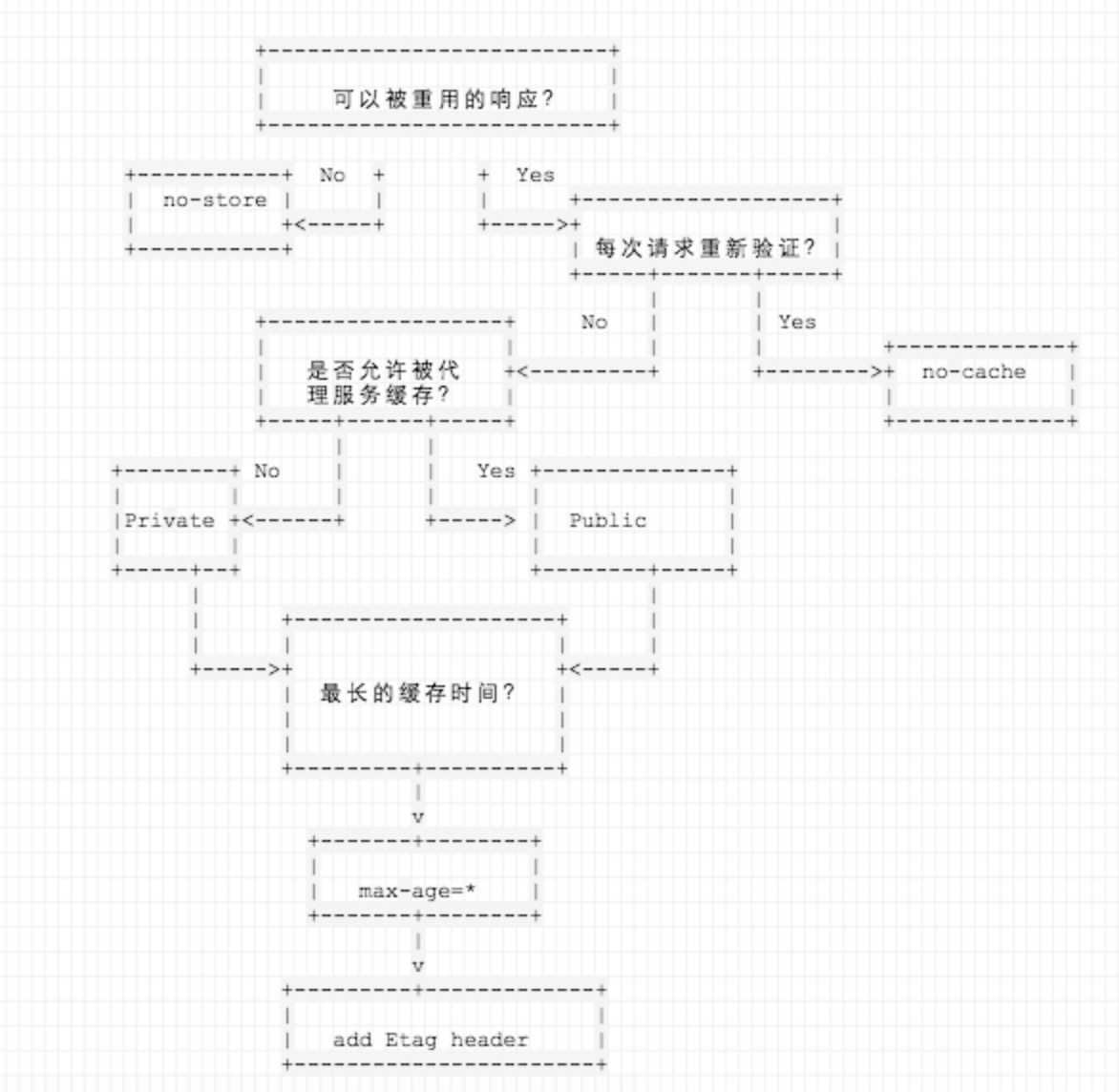
客户端的新鲜度限值
Cache-Control不仅仅可以在响应头中设置,还可以在请求头中设置。浏览器通过请求头中设置Cache-Control可以决定是否从缓存中读取资源。这也是为什么有时候点击浏览器刷新按钮和在地址栏回车,在NetWork模块中看到完全不同的结果
Expires
不推荐使用Expires,它指定的是具体的过期日期而不是秒数。因为很多服务器跟客户端存在时钟不一致的情况,所以最好还是使用Cache-Control.
服务器再验证
浏览器或代理缓存中缓存的资源过期了,并不意味着它和原始服务器上的资源有实际的差异,仅仅意味着到了要进行核对的时间了。这种情况被称为服务器再验证。
如果资源发生变化,则需要取得新的资源,并在缓存中替换旧资源。
如果资源没有发生变化,缓存只需要获取新的响应头,和一个新的过期时间,对缓存中的资源过期时间进行更新即可。
HTTP1.1推荐使用的验证方式是If-None-Match/Etag,在HTTP1.0中则使用If-Modified-Since/Last-Modified。
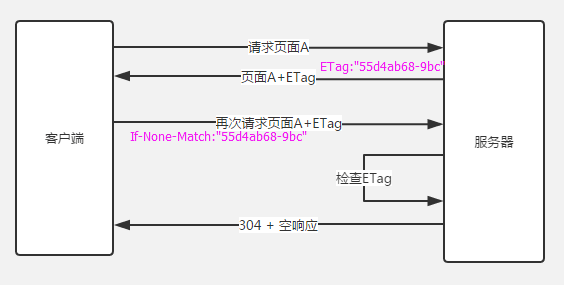
Etag与If-None-Match
根据实体内容生成一段hash字符串,标识资源的状态,由服务端产生。浏览器会将这串字符串传回服务器,验证资源是否已经修改,如果没有修改,过程如下(图片来自浅谈Web缓存):
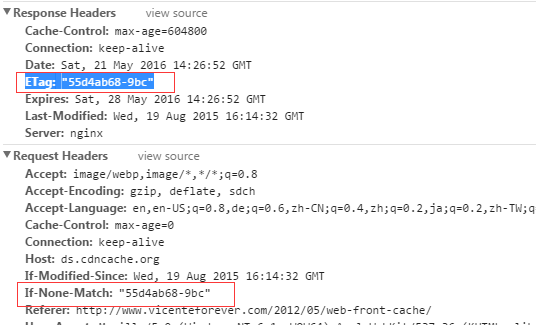
上文的demo中我们见到过服务器端如何验证Etag:
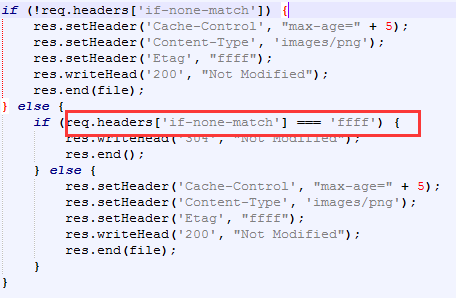
由于Etag有服务器构造,所以在集群环境中一定要保证Etag的唯一性
If-Modified-Since与Last-Modified
这两个是HTTP1.0中用来验证资源是否过期的请求/响应头,这两个头部都是日期,验证过程与Etag类似,这里不详细介绍。使用这两个头部来验证资源是否更新时,存在以下问题:
有些文档资源周期性的被重写,但实际内容没有改变。此时文件元数据中会显示文件最近的修改日期与If-Modified-Since不相同,导致不必要的响应。
有些文档资源被修改了,但修改内容并不重要,不需要所有的缓存都更新(比如代码注释)
关于缓存的更新问题,请大家看看这里张云龙的回答,本文就不详细展开了。
本文demo代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE HTML><html> <head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=no" /><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=EDGE" /><title>Web Cache</title><link rel="shortcut icon" href="./shortcut.png"><script></script> </head> <body class="claro"> <img src="./cache.png"> </body></html>var http = require("http");var fs = require("fs");http.createServer(function(req, res) {if (req.url === "/" || req.url === "" || req.url === "/index.html") {fs.readFile("./index.html", function(err, file) {console.log(req.url)//对主文档设置缓存,无效果res.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache, max-age=" + 5);res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html");res.writeHead("200", "OK");res.end(file);});}if (req.url === "/shortcut.png") {fs.readFile("./shortcut.png", function(err, file) {console.log(req.url)res.setHeader("Content-Type", "images/png");res.writeHead("200", "OK");res.end(file);})}if (req.url === "/cache.png") {fs.readFile("./cache.png", function(err, file) {console.log(req.headers);console.log(req.url)if (!req.headers["if-none-match"]) {res.setHeader("Cache-Control", "max-age=" + 5);res.setHeader("Content-Type", "images/png");res.setHeader("Etag", "ffff");res.writeHead("200", "Not Modified");res.end(file);} else {if (req.headers["if-none-match"] === "ffff") {res.writeHead("304", "Not Modified");res.end();} else {res.setHeader("Cache-Control", "max-age=" + 5);res.setHeader("Content-Type", "images/png");res.setHeader("Etag", "ffff");res.writeHead("200", "Not Modified");res.end(file);}}});}}).listen(8888)好了,本文关于cookie的介绍到此结束了,希望大家能够喜欢。