//创建学生对象Student student=new Student();student.setAge(23);student.setClazz("六年级");student.setName("王二麻子");//创建JSONObject JSONObject jsonObject=new JSONObject();//键值对赋值jsonObject.put("age",student.getAge());jsonObject.put("name",student.getName());jsonObject.put("clazz",student.getClazz());//转化成json字符串String json=jsonObject.toString(); //输出日志Log.e("ObjectToJson",json);Log日志显示

json转对象
新建一个JSONObject 把json串通过构造方法赋值 这个JSONObject 对象就带有json的值 然后创建对象 一个一个赋值 JSONObject 对于不同类型的值 有不同的get方法
JSONObject jsonObject=new JSONObject(json); Student student=new Student(); student.setName(jsonObject.getString("name")); student.setClazz(jsonObject.getString("clazz")); student.setAge(jsonObject.getInt("age")); Log.e("JsonToObject",student.getName()+"======"+student.getClazz()+"===="+student.getAge());

List转json
使用JONSArray
//创建一个集合List<Student> students=new ArrayList<Student>();students.add(student);students.add(student);//创建一个JSONArray JSONArray jsonArray=newJSONArray();//遍历学生集合for(inti=0;i<students.size();i++){ //获取学生对象 Studentstu=students.get(i); //创建JSONObject JSONObject jo=newJSONObject(); //赋值 jo.put("age",stu.getAge()); jo.put("name",stu.getName()); jo.put("clazz",stu.getClazz()); //把JSONObject 添加到JSONArray jsonArray.put(jo);}//toString转为jsonString json=jsonArray.toString();Log.e("ListToJson",json);
json转List
//创建JSONArray把json传入JSONArray jsonArray=new JSONArray(json);//创建学生集合Student students=new ArrayList<Student>();Log.e("BeforeJsonToList","集合长度"+students.size());//遍历jsonArrayfor(inti=0;i<jsonArray.length();i++){ //获取JSONObject对象 JSONObject jsonObject=jsonArray.getJSONObject(i); //创建学生对象 Student stu=new Student(); //赋值 jsonObject.put("age",stu.getAge()); jsonObject.put("name",stu.getName()); jsonObject.put("clazz",stu.getClazz()); //把学生对象添加到集合中 students.add(stu);}Log.e("AfterJsonToList","集合长度"+students.size());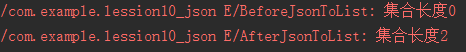
注意 :在使用JSONObject和JSONArray的过程中是需要捕获异常的
有没有感觉很麻烦,这要是数据多了简直是要累死人了
变简单的方法就是下载一个号称史上最快json操作的fastjson.jar 阿里出品 然后使用就简单了
FastJson操作数据
对象转json
//创建学生对象Student student=new Student();student.setClazz("一班");student.setAge(23);student.setName("李四");//将对象转为json串String json=JSON.toJSONString(student);Log.e("ObjectToJson",json);只有一句话 就完成了 简单到爆有没有 感谢马云粑粑!!!

json转对象
//将json转为对象 参数1json 参数2对象类型 Student student=JSON.parseObject(json,Student.class); Log.e("JsonToObject","=========="+student.getName());同样只有一句话 相对于android原生真是感人

list转json
List<Student>stuList=new ArrayList<Student>();stuList.add(student);stuList.add(student);stuList.add(student);//List集合转jsonjson=JSON.toJSONString(stuList);Log.e("ListToJson","=========="+json);集合中添加了三个同一个对象 json字符串的输出 就变成了 ref,{0} 很明显这是引用第一个对象 因为你添加了相同的对象 fastjson就不创建了 直接引用 这也是他号称最快的原因
json=JSON.toJSONString(stuList,SerializerFeature.DisableCircularReferenceDetect);
json转list
stuList=JSON.parseArray(json,Student.class); Student student1=stuList.get(0); Log.e("JsonToList","====================="+student1.getName());

有时候呢 并不需要对象里的所有字段 这时候就可以设置一个属性过滤器 把你不需要的字段过滤掉
//过滤字段 属性过滤器PropertyFilterjson=JSON.toJSONString(stuList, new PropertyFilter() {@Override//参数1 正在被过滤的对象 参数2 过滤的属性名 参数3 属性值public boolean apply(Object o, String s, Object o1) {Log.e("PropertyFilter",o+"======"+s+"==============="+o1);if (s.equals("name")){return false;}else{return true;}}});Log.e("PropertyFilter",json);设置name过滤 请看log日志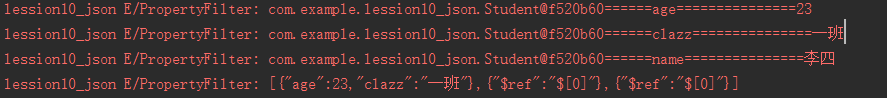
在介绍一种情况
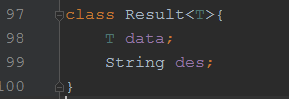
定义了一个泛型类
里面有一个学生对象 和一个字符串
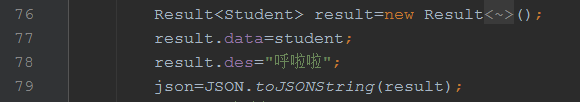
把对象转json
当我们要把这个json转为对象的时候问题就来了

这时候就需要实现TypeReference类 把对象封装一下

完美解决 凡是带泛型的都可以使用TypeReference

最后给大家介绍一个网站 http://json.cn/ 特别强大 会自动格式化json 如果有语法错误也会报错滴
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作能带来一定的帮助,同时也希望多多支持脚本之家!