Android程序中,Tab标签窗口是一种常用的UI界面元素。它的实现主要是利用了TabHost类。
TabHost说明TabHost是一个标签窗口的容器。
一个TabHost对象包含两个子元素对象:
一个对象是tab标签集合(TabWidget),用户点击它们来选择一个特定的标签;
另一个是FrameLayout对象,展示当前页的内容。
子元素通常是通过容器对象来控制,而不是直接设置子元素的值。
下面结合ApiDemos中的例子来说明TabHost的用法。
第一个Tab例子:使用TabActivity这个例子使用了 TabActivity。
Java程序代码:
package com.meng.hellotab;import android.os.Bundle;import android.view.LayoutInflater;import android.widget.TabHost;import android.app.TabActivity;@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")public class HelloTabActivity extends TabActivity{@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState){super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);// 得到TabActivity中的TabHost对象TabHost tabHost = getTabHost();// 内容:采用布局文件中的布局LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.activity_hello_tab,tabHost.getTabContentView(), true);// 加上标签// 参数设置:新增的TabSpec的标签,标签中显示的字样// setContent设置内容对应的View资源标号tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1").setIndicator("tab1 indicator").setContent(R.id.view1));tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3").setIndicator("tab2").setContent(R.id.view2));tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3").setIndicator("tab3").setContent(R.id.view3));}}其中布局文件如下:
布局文件1
布局文件1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent" ><TextViewandroid:id="@+id/view1"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:background="@drawable/blue"android:text="@string/tab1" /><TextViewandroid:id="@+id/view2"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:background="@drawable/red"android:text="@string/tab2" /><TextViewandroid:id="@+id/view3"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:background="@drawable/green"android:text="@string/tab3" /></FrameLayout>
布局文件中的颜色字符串如下:文本字符串略。
colors.xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><resources><drawable name="red">#7f00</drawable><drawable name="blue">#770000ff</drawable><drawable name="green">#7700ff00</drawable><drawable name="yellow">#77ffff00</drawable><drawable name="screen_background_black">#ff000000</drawable><drawable name="translucent_background">#e0000000</drawable><drawable name="transparent_background">#00000000</drawable><color name="solid_red">#f00</color><color name="solid_blue">#0000ff</color><color name="solid_green">#f0f0</color><color name="solid_yellow">#ffffff00</color></resources>
运行截图:
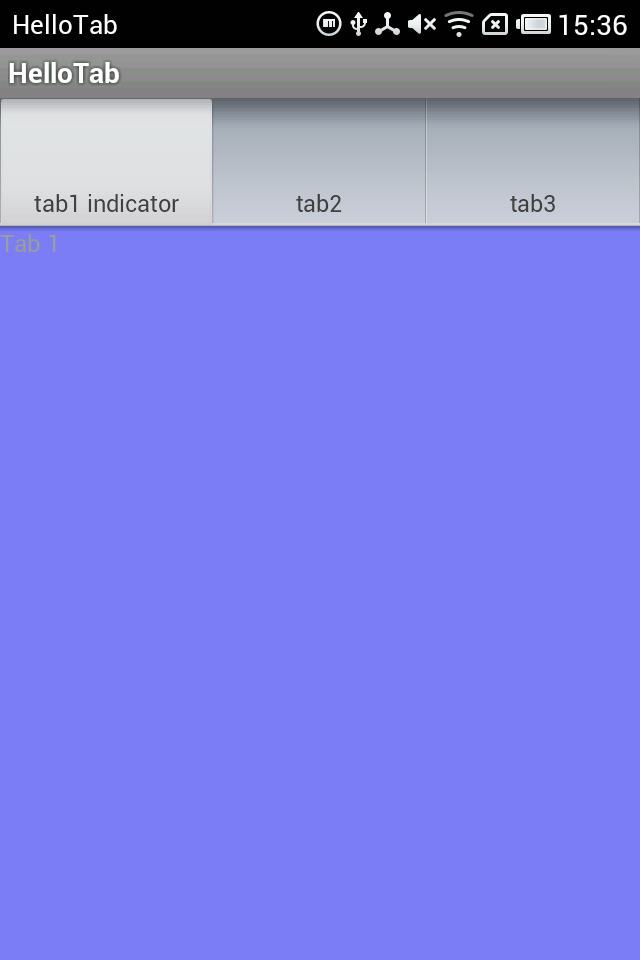
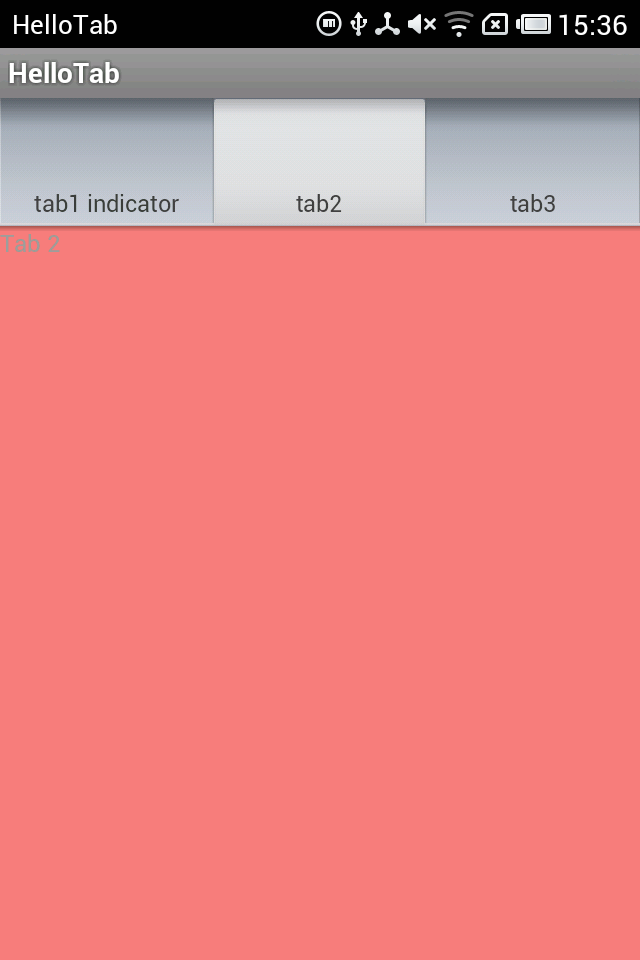
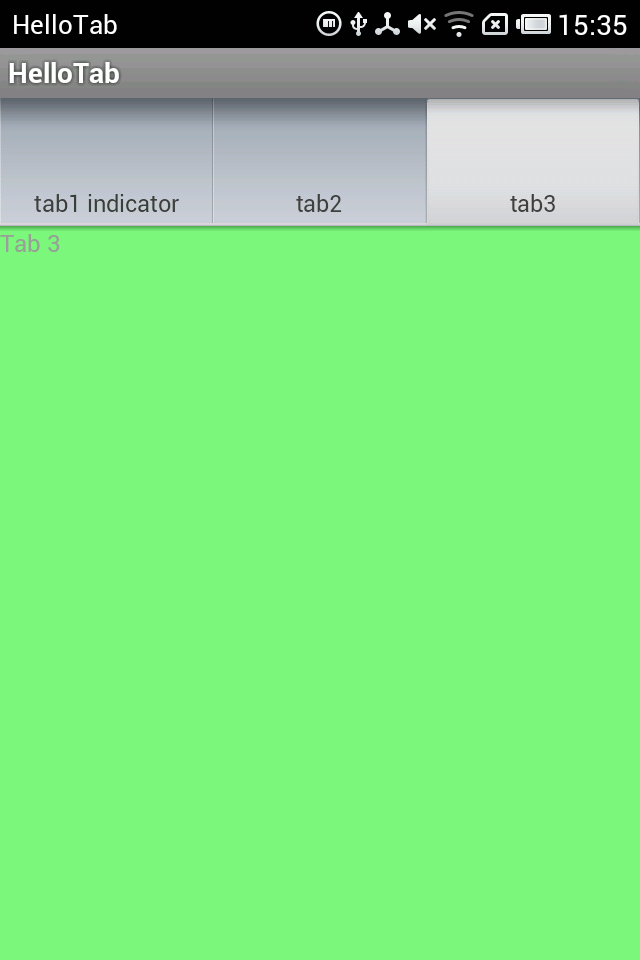
注意 TabActivity这个类已经被标注为:This class was deprecated in API level 13。
第二个程序:使用TabHost.TabContentFactoryTabHost.TabContentFactory这个接口是用来在tab被选择时自己创建内容,而不是显示一个已经存在的view或者启动一个activity,这两种要用其他的方法。
具体实现见代码:
package com.meng.hellotab;import android.os.Bundle;import android.view.LayoutInflater;import android.view.View;import android.widget.TabHost;import android.widget.TextView;import android.app.TabActivity;@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")public class HelloTabActivity extends TabActivity implementsTabHost.TabContentFactory{@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState){super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);TabHost tabHost = getTabHost();// 不再需要载入布局文件,如果此句不注释掉会导致content的重叠// LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.activity_hello_tab,// tabHost.getTabContentView(), true);// setContent中传递thistabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1").setIndicator("tab1 indicator").setContent(this));tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3").setIndicator("tab2").setContent(this));tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3").setIndicator("tab3").setContent(this));}// setContent的参数设为this时,从这个方法得到每一个Tab的内容(此次不用布局文件,用的话会重叠)@Overridepublic View createTabContent(String tag){// 参数: 这个方法会接受到被选择的tag的标签final TextView tv = new TextView(this);tv.setText("Content for tab with tag " + tag);return tv;}}程序运行截图:
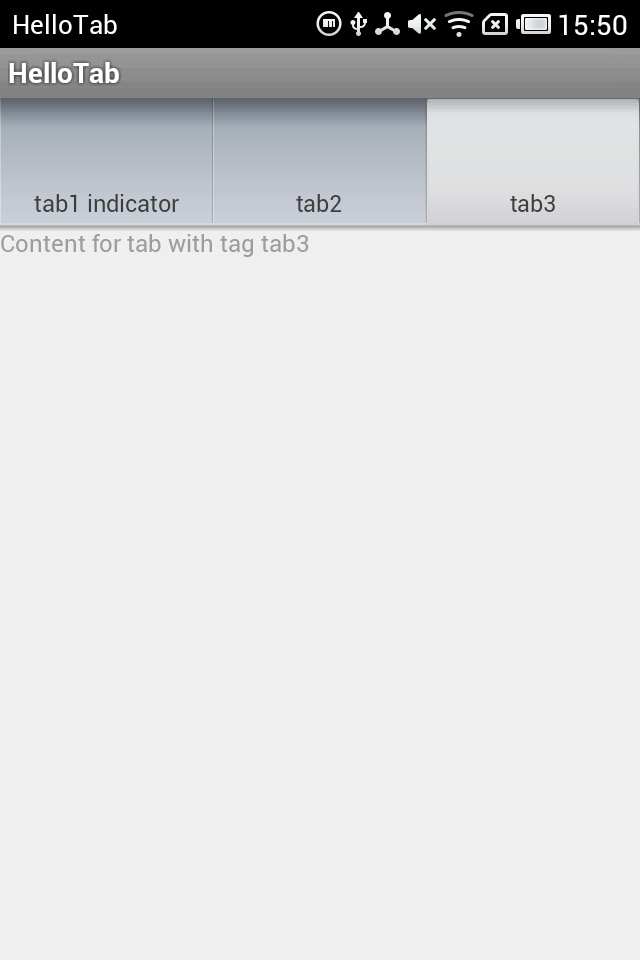
另外,Tab的content的内容还可以启动另一个Activity,只要在setContent方法中传入一个Intent即可。
此部分不再介绍,可以参见ApiDemos中的Tabs3.java代码。
第三个程序:不继承TabActivity前面两个程序例子中都是继承了TabActivity类,如果不继承它,需要自己写TabHost的布局,其中包含了两个必要的子元素:TabWidget和FrameLayout,其id都是固定值,见代码。
布局文件代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:orientation="vertical" ><TextViewandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="@string/hello_world" /><!-- TabHost必须包含一个 TabWidget和一个FrameLayout --><TabHostandroid:id="@+id/myTabHost"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent" ><LinearLayoutandroid:layout_width="fill_parent"android:layout_height="fill_parent"android:orientation="vertical" ><!-- TabWidget的id属性必须为 @android:id/tabs --><TabWidgetandroid:id="@android:id/tabs"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_weight="0"android:orientation="horizontal" /><!-- FrameLayout的id属性必须为 @android:id/tabcontent --><FrameLayoutandroid:id="@android:id/tabcontent"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:layout_weight="0" ><TextViewandroid:id="@+id/view1"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:text="Tab1 Content" /><TextViewandroid:id="@+id/view2"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:text="Tab2 Content" /><TextViewandroid:id="@+id/view3"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:text="Tab3 Content" /></FrameLayout></LinearLayout></TabHost></LinearLayout>
Activity代码:
package com.meng.hellotabhost;import android.os.Bundle;import android.app.Activity;import android.view.Menu;import android.widget.TabHost;public class HelloTabHostActivity extends Activity{@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState){super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_hello_tab_host);TabHost tabHost = (TabHost) findViewById(R.id.myTabHost);// 如果不是继承TabActivity,则必须在得到tabHost之后,添加标签之前调用tabHost.setup()tabHost.setup();// 这里content的设置采用了布局文件中的viewtabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1").setIndicator("tab1 indicator").setContent(R.id.view1));tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3").setIndicator("tab2").setContent(R.id.view2));tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3").setIndicator("tab3").setContent(R.id.view3));}}这种方式可以实现比较灵活的布局,可以方便地加入其他组件,还可以改变标签栏和内容栏的相对位置。
第四个程序:scrolling Tab当标签太多时,需要把标签设置进一个ScrollView中进行滚动。有了上面的程序做基础,这个很好理解。
ApiDemos中给出的仍然是继承TabActivity的方法,在这里给出另一种不用继承TabActivity的方法,两种方法很类似。
布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:orientation="vertical" ><TabHostandroid:id="@+id/myTabHost"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent" ><LinearLayoutandroid:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:orientation="vertical"android:padding="5dp" ><HorizontalScrollViewandroid:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:scrollbars="none" ><TabWidgetandroid:id="@android:id/tabs"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content" /></HorizontalScrollView><FrameLayoutandroid:id="@android:id/tabcontent"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:padding="5dp" /></LinearLayout></TabHost></LinearLayout>
Java代码:
package com.meng.hellotabscroll;import android.os.Bundle;import android.app.Activity;import android.view.View;import android.widget.TabHost;import android.widget.TextView;public class HelloTabScrollActivity extends Activity implementsTabHost.TabContentFactory{@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState){super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_hello_tab_scroll);// 从布局中获取TabHost并建立TabHost tabHost = (TabHost) findViewById(R.id.myTabHost);tabHost.setup();// 加上30个标签for (int i = 1; i <= 30; i++){String name = "Tab " + i;tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec(name).setIndicator(name).setContent(this));}}@Overridepublic View createTabContent(String tag){final TextView tv = new TextView(this);tv.setText("Content for tab with tag " + tag);return tv;}}以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。



