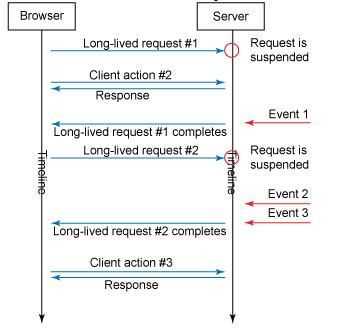
它的实现过程如下:页面加载的时候随即向服务器发送一条Ajax请求,服务器端获取请求并将它保存在一个线程安全的容器中(通常为队列)。同时服务器端仍然可以正常响应其他请求。当需要推送的事件到来的时候,服务器遍历容器中的请求在返回应答后删除。于是所有停留在页面中的浏览器都会获得该应答,并再次发送Ajax请求,重复上述过程。
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"pageEncoding="UTF-8"%><%String path = request.getContextPath();String basePath = request.getScheme() + "://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort()+ path + "/";%><!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><base href="<%=basePath%>"><head><title>WebSocket</title><script type="text/javascript" src="static/jquery-1.9.1.min.js"></script><script type="text/javascript">$(function() {connect();$("#btn").click(function() {var value = $("#message").val();$.ajax({url : "longpolling?method=onMessage&msg=" + value,cache : false,dataType : "text",success : function(data) {}});});});function connect() {$.ajax({url : "longpolling?method=onOpen",cache : false,dataType : "text",success : function(data) {connect();alert(data);}});}</script></head><body><h1>LongPolling</h1><input type="text" id="message" /><input type="button" id="btn" value="发送" /></body></html> 我们注意到,由btn发送的请求其实并不需要获取应答。整个过程的关键是需要客户端始终让服务器保持connect()的请求。而服务器端首先需要支持这种异步的响应方式,幸运的是目前为止绝大部分的Servlet容器都已经提供了良好的支持。下面以Tomcat为例:package servlet;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.PrintWriter;import java.util.Queue;import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue;import javax.servlet.AsyncContext;import javax.servlet.ServletException;import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;@WebServlet(value="/longpolling", asyncSupported=true)public class Comet extends HttpServlet {private static final Queue<AsyncContext> CONNECTIONS = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<AsyncContext>();@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {String method = req.getParameter("method");if (method.equals("onOpen")) {onOpen(req, resp);} else if (method.equals("onMessage")) {onMessage(req, resp);}}private void onOpen(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {AsyncContext context = req.startAsync();context.setTimeout(0);CONNECTIONS.offer(context);}private void onMessage(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {String msg = req.getParameter("msg");broadcast(msg);}private synchronized void broadcast(String msg) {for (AsyncContext context : CONNECTIONS) {HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) context.getResponse();try {PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();out.print(msg);out.flush();out.close();context.complete();CONNECTIONS.remove(context);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}} ConcurrentLinkedQueue是Queue队列的一个线程安全实现,这里使用它来作为保存请求的容器。AsyncContext是Tomcat支持的异步环境,不同的服务器使用的对象也略有不同。Jetty支持的对象是Continuation。完成了广播的请求需要通过context.complete()将相关请求结束,并使用CONNECTIONS.remove(context)删除队列。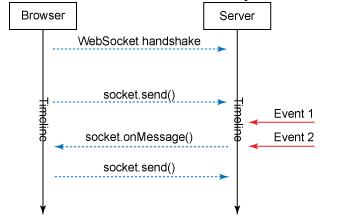
首先:WebSockets并非在所有浏览器上都能获得良好的支持,显然IE又拖了后腿。因此当你打算使用这项技术之前必须考虑到用户的使用环境,如果你的项目面向的是互联网或者包括手机端用户,奉劝大家三思。
其次:WebSockets提供的请求区别于普通的HTTP请求,它是一种全双工通信且始终处于激活状态(如果你不去关闭它的话)。这就意味着你不用每次获得应答后再次向服务器发送请求,这样可以节约大量的资源。
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"pageEncoding="UTF-8"%><%String path = request.getContextPath();String basePath = request.getScheme() + "://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort()+ path + "/";String ws = "ws://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort() + path + "/";%><!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><base href="<%=basePath%>"><head><title>WebSocket</title><script type="text/javascript" src="static/jquery-1.9.1.min.js"></script><script type="text/javascript">$(function() {var websocket = null;if ("WebSocket" in window){websocket = new WebSocket("<%=ws%>websocket");} else {alert("not support");}websocket.onopen = function(evt) {}websocket.onmessage = function(evt) {alert(evt.data);}websocket.onclose = function(evt) {}$("#btn").click(function() {var text = $("#message").val();websocket.send(text);});});</script></head><body><h1>WebSocket</h1><input type="text" id="message" /><input type="button" id="btn" value="发送"/></body></html> JQuery对WebSocket还未提供更良好的支持,因此我们必须使用Javascript来编写部分代码(好在并不复杂)。并且打部分常见的服务器都可以支持ws请求,以Tomcat为例。在6.0版本中WebSocketServlet对象已经被标注为@java.lang.Deprecated,7.0以后的版本支持jsr365提供的实现,因此你必须使用注解来完成相关配置。package servlet;import java.io.IOException;import java.util.Queue;import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue;import javax.websocket.OnClose;import javax.websocket.OnMessage;import javax.websocket.OnOpen;import javax.websocket.Session;import javax.websocket.server.ServerEndpoint;@ServerEndpoint("/websocket")public class WebSocket {private static final Queue<WebSocket> CONNECTIONS = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<WebSocket>();private Session session;@OnOpenpublic void onOpen(Session session) {this.session = session;CONNECTIONS.offer(this);}@OnMessagepublic void onMessage(String message) {broadcast(message);}@OnClosepublic void onClose() {CONNECTIONS.remove(this);}private synchronized void broadcast(String msg) {for (WebSocket point : CONNECTIONS) {try {point.session.getBasicRemote().sendText(msg);} catch (IOException e) {CONNECTIONS.remove(point);try {point.session.close();} catch (IOException e1) {}}}}} 三、总结(从请求到推送)