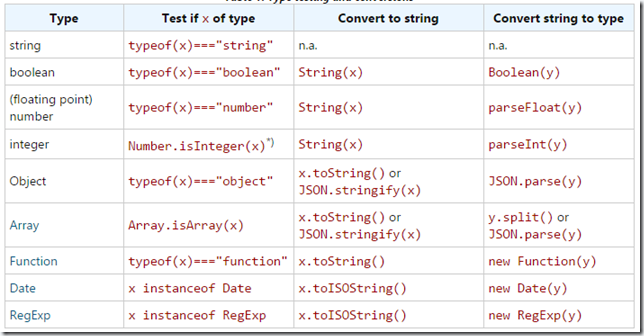
if (firstName + lastName === "James Bond") ...numeric 表示64位的浮点数,在JS 中没有明显的区分整形和浮点数,如果一个表达式的值不等于某个数字,那么它的值可设为NaN,表示非数字,可联合isNaN使用。
二、变量作用域范围
目前,JavaScript,ES5提供两种作用域类型:全局变量及函数作用域,没有块作用域。块作用域的范围不太明确,所以应当避免块作用域的使用。如下代码,尽管是开发人员常用的Pattern,却是一个陷阱。
function foo() { for (var i=0; i < 10; i++) { ... // do something with i }}所有的变量声明最好是在函数的开始位置。在JS,ES6版本中支持块作用域,采用关键字let 定义变量。var person1 = { lastName:"Smith", firstName:"Tom"};var o1 = Object.create( null); // an empty object with no slots如果Slot 的name 是合法的JS 标识符,则Slot可表示属性,方法,或键值对。如果名称含有一些特殊字符如空格,则Slot代表键值对,是一种映射元素,如下:person1.lastName = "Smith"2. 使用map:
person1["lastName"] = "Smith"JS 对象能够用于各种途径,以下是五种常见情况:
var myRecord = {firstName:"Tom", lastName:"Smith", age:26}2. map 如Hash map,数组,hash表;var numeral2number = {"one":"1", "two":"2", "three":"3"}3. Untyped 对象不需要实例化类,它可能包含property slot 和function slots:var person1 = {lastName: "Smith",firstName: "Tom", getFullName: function () { return this.firstName +" "+ this.lastName;} };Array ListJS array 即逻辑数据结构,通过数组下标访问。如数组初始化:var i=0;for (i=0; i < a.length; i++) { console.log( a[i]);}如果数组较小,可使用foreach 循环:a.forEach( function (elem) { console.log( elem);}) JS 也提供克隆数组的函数:var clone = a.slice(0);三、Maps
var myTranslation = {"my house": "mein Haus","my boat": "mein Boot","my horse": "mein Pferd"}增加: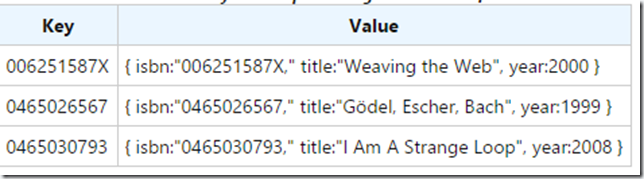
record,map,entity 在实际应用中没有明显的区分,只是概念上的区分。对JS 引擎而言,都是对象。但是从概念上是有区分的。
四、函数
如表1 所示,函数是特殊的JS 对象,有name 属性和length属性表示参数的个数,如下,判断v是否指向函数:
if (typeof( v) === "function") {...}函数定义:var myFunction = function theNameOfMyFunction () {...}theNameOfMyFunction 是可选的,如果省略函数名称,则称该函数为匿名函数。通常,函数是通过变量来调用的,如上面的代码,则表示var list = [[1,2],[1,3],[1,1],[2,1]]; list.sort( function (x,y) {return ((x[0] === y[0]) ? x[1]-y[1] : x[0]-y[0]);});函数声明:function theNameOfMyFunction () {...}与代码var theNameOfMyFunction = function theNameOfMyFunction () {...}等价;var sum = function (numbers) { var result = 0; numbers.forEach( function (n) { result += n; }); return result;};console.log( sum([1,2,3,4]));当执行一个方法时,可以使用内置arguments 对象访问函数内的参数,arguments 对象与数组使用方法类似,有长度属性,也有索引,并且可以使用For语句来循环迭代。但是由于它并不是Array 实例,因此JS arrary的部分方法无法应用如foreach。var sum = function () { var result = 0, i=0; for (i=0; i < arguments.length; i++) { result = result + arguments[i]; } return result;};console.log( sum(0,1,1,2,3,5,8)); // 20方法是在构造函数的原型上定义的,可以通过对象创建的构造器调用,如Array.prototype.forEach;Array表示构造器,调用类的实例作为上下文对象参考的,如下: 在foreach中numbers表示上下文对象:var numbers = [1,2,3]; // create an instance of Arraynumbers.forEach( function (n) { console.log( n);});无论原型方法是否被上下文对象调用,但是只要是参数为对象,可以使用JS函数的Call 方法来辅助调用对象。如下,我们可以使用foreach 循环方法:var sum = function () { var result = 0; Array.prototype.forEach.call( arguments, function (n) { result = result + n; }); return result;};Function.prototype.call方法和apply都是为了改变某个函数运行时的 context 即上下文而存在的。class Person { constructor( first, last) { this.firstName = first; this.lastName = last; } toString() { return this.firstName + " " + this.lastName; } static checkLastName( ln) { if (typeof(ln)!=="string" ||ln.trim()==="") { console.log("Error: " +"invalid last name!"); } }}Step 1.b 类层次的属性定义:class Student extends Person { constructor( first, last, studNo) { super.constructor( first, last); this.studNo = studNo;} // method overrides superclass method toString() { return super.toString() + "(" + this.studNo +")"; }}ES5中,可以定义继承基于构造器类的子类。如下:function Person( first, last) { this.firstName = first;this.lastName = last; }注意,上述代码中的this 指的是新生成的对象,当构造函数被调用时,该对象就已经生成了。Person.prototype.toString = function () { return this.firstName + " " + this.lastName;}Step 1.c 定义静态方法:Person.checkLastName = function (ln) { if (typeof(ln)!=="string" || ln.trim()==="") { console.log("Error: invalid last name!"); }}Step 1.d 定义类层次的静态属性Person.instances = {};Step 2.a 定义子类:// Student inherits from PersonStudent.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype);// adjust the subtype"s constructor propertyStudent.prototype.constructor = Student;Step2c, 重新定义子类方法重写超类方法:
Student.prototype.toString = function () { return Person.prototype.toString.call( this) + "(" + this.studNo + ")";};基于构造器类的实例化是通过应用new 操作符来创建的,并提供合适的构造参数:var pers1 = new Person("Tom","Smith");方法toString 通过pers1. 来调用:
alert("The full name of the person are: " +pers1.toString());在JS中,prototype 是具有method slots 的对象,可以通过JS方法或属性槽继承的。
var Person = { name: "Person", properties: { firstName: {range:"NonEmptyString", label:"First name",writable: true, enumerable: true}, lastName: {range:"NonEmptyString", label:"Last name",writable: true, enumerable: true} }, methods: { getFullName: function () { return this.firstName +" "+ this.lastName;} }, create: function (slots) { // create object var obj = Object.create( this.methods, this.properties); // add special property for *direct type* of object Object.defineProperty( obj, "type",{value: this, writable: false, enumerable: true}); // initialize object Object.keys( slots).forEach( function (prop) { if (prop in this.properties) obj[prop] = slots[prop]; }) return obj; }};注意JS对象Person实际表示的是factory-based 类。factory-based类的实例化是通过调用它自己的Create方法实现的: