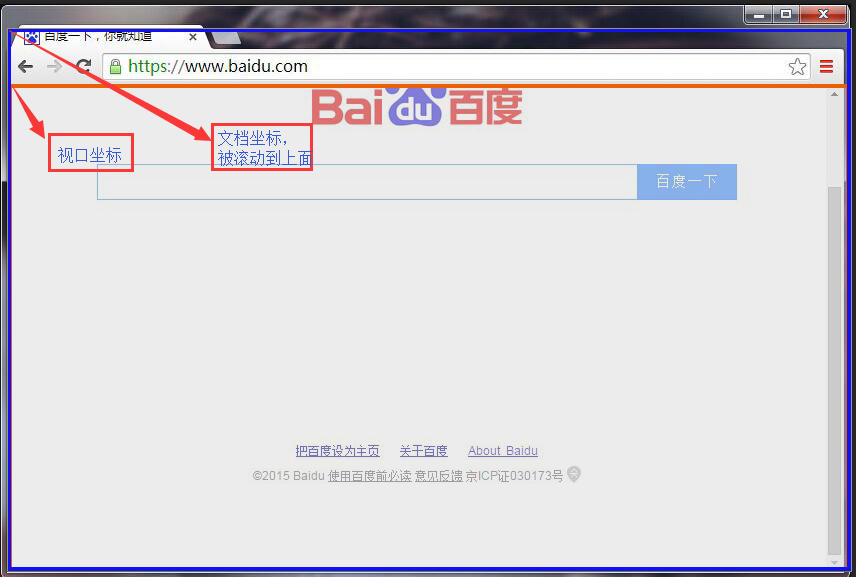

为了在坐标系中转换,我们需要判定浏览器窗口的滚动条的位置。Window对象的pageXoffset和pageYOffset属性在所有的浏览器中提供这些值,除了IE8及更早的版本以外。IE(和所有现代浏览器)也可以通过scrollLeft和scrollTop属性来获得滚动条的位置。令人迷惑的是,正常的情况下通过查找文档的根节点(document.documentElement)来获取这些属性,但是在怪异模式下,必须在文档的<body>元素(documeng.body)上查询它们。以下显示了如何简便的查询滚动条的位置。
functon getScrollOffsets(w){w = w || window;var sLeft,sTop;if(w.pageXOffset != null) {sLeft = w.pageXOffset;sTop = w.pageYOffset;return {x:sLeft,y:sTop};}if(document.compatMode == "CSS1Compat"){sLeft = document.documentElement.scrollLeft == 0 ? document.body.scrollLeft : document.documentElement.scrollLeft; sTop = document.documentElement.scrollTop == 0 ? document.body.scrollTop : document.documentElement.scrollTop;return {x:sLeft,y:sTop};}else if(document.compatMode == "BackCompat"){sLeft = document.body.scrollLeft; sTop = document.body.scrollTop;return {x:sLeft,y:sTop};}}有时候能够判定视口的尺寸也是非常有用的,例如,为了确定文档的案部分是当前可见的。利用滚动偏移量查询视口的尺寸的简单方法在IE8及更早版本中无法工作,而且该技术在IE中的运行法师还要取决于浏览器是否处于怪异模式还是标准模式。function getViewportSize(w){ w = w || window; var cWidth,cHeight; if(w.innerWidth != null){ cWidth = w.innerWidht; cHeight = w.innerHeight; return {w:cWidth,h:w.cHeight}; } if(document.compatMode == "CSS1Compat"){ cWidth = document.documentElement.clientWidth; cHeight = doument.documentElement.clientHeight; return {w:cWidth,h:w.cHeight}; }else if(document.compatMode == "BackCompat"){ cWidth = document.body.clientWidth; cHeight = doument.body.clientHeight; return {w:cWidth,h:w.cHeight}; }}